Yes, sharks do poop. In order to understand sharks’ bathroom habits, it is important to delve into their digestive system and feeding patterns.
Sharks have a simple and efficient digestive system that allows them to efficiently process the food they consume. As they eat, sharks break down the food in their stomach and absorb the nutrients. The waste, or feces, is then eliminated through the rectal opening located near the anal fins.
These shark droppings consist mainly of indigestible parts such as bones, skin, and cartilage. The size and frequency of shark poop varies depending on the species and its diet, but it is an essential part of their biological process.
Exposing The Truth: Yes, Sharks Do Poop!
Despite the myths surrounding sharks and their waste, there is no denying the truth – sharks do poop. In this section, we will debunk the myths surrounding shark waste and delve into the frequency and characteristics of their poop.
Debunking The Myths Surrounding Shark Waste
Contrary to popular belief, sharks are not mystical beings that absorb every bit of their prey’s flesh, leaving no trace behind. Here are some key points to debunk the myths surrounding shark waste:
- Sharks, like all animals, need to eliminate waste from their bodies. While their digestion process is efficient, they still produce fecal matter.
- The idea that sharks do not poop may have originated from the misconception that their bodies completely break down consumed prey, leaving nothing behind.
- Just like any other animal, sharks have a digestive system designed to extract nutrients from their food. They excrete waste materials that their bodies cannot absorb or utilize.
Understanding The Frequency And Characteristics Of Shark Poop
Sharks’ digestive systems vary depending on their species, size, and diet. Consequently, the frequency of their bowel movements can differ. However, sharks typically excrete waste regularly.
The appearance of shark poop can vary depending on their diet. Sharks generally have a high-protein diet, which results in dark, compact fecal matter. It may resemble a twisted rope or even a spiral due to the shape of their intestines.
One peculiar characteristic of shark feces is its high calcium content. Since sharks have no real bones, their skeletons are made of cartilage. This leads to a higher calcium concentration in their waste, making it beneficial for marine ecosystems.
The Importance Of Shark Waste In Marine Ecosystems

Shark waste is a valuable resource that contributes significantly to the health and functioning of marine ecosystems. Let’s delve deeper into the significance of shark waste in marine ecosystems.
Exploring The Ecological Significance Of Shark Waste
Sharks, being apex predators, have a profound impact on their environment. Here’s how their waste contributes to nutrient cycling in the ocean:
- Rich in nutrients: Shark waste, also known as shark feces or scat, is packed with essential nutrients. It contains a high concentration of nitrogen, phosphorus, and other organic matter that can fertilize marine ecosystems.
- Aid in nutrient redistribution: When sharks defecate, the nutrients in their waste spread throughout the water, providing nourishment to phytoplankton, algae, and other small organisms. This redistribution helps maintain a healthy balance in the underwater food chain.
- Stimulate algal blooms: The nutrients from shark waste can stimulate the growth of algal blooms. These blooms are essential for filtering toxins, producing oxygen, and providing food for countless marine organisms, including fish and invertebrates.
- Support marine biodiversity: Algal blooms, fueled by the nutrients from shark waste, support a diverse array of marine life. From small fish to large whale sharks, these ecosystems provide a habitat for countless species, promoting biodiversity and ensuring the survival of marine ecosystems.
- Contribute to carbon sequestration: Besides aiding nutrient cycling, shark waste also plays a role in carbon sequestration. Algae and other photosynthetic organisms fueled by the nutrients in shark waste absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Is Shark Waste Similar To Other Marine Animals?
While sharks do indeed produce waste, it is different from that of other marine animals in terms of composition, volume, and environmental impact.
Here are the key points to consider when comparing the waste products of sharks with other marine animals:
- Digestive efficiency: Sharks have highly efficient digestive systems, allowing them to extract maximum nutrients from their prey. As a result, their waste tends to be relatively low in volume compared to other marine animals.
- Composition: Shark waste primarily consists of partially digested food, undigested prey parts, and indigestible materials such as cartilage and bone. This composition is quite different from the waste produced by other marine animals.
- Smell: Contrary to popular belief, shark waste does not have a distinct odor. In fact, it is often difficult to detect the presence of shark waste in the ocean due to its low volume and fast dispersion.
- Elimination: Sharks eliminate waste through their cloaca, a single opening that serves as an exit for both waste and reproductive materials. This efficient elimination process ensures that waste is quickly released into the water, minimizing any potential pollution.
- Environmental impact: While shark waste itself does not pose a significant environmental threat, the large quantities of waste produced by other marine animals can have a significant impact on the ecosystem. For example, large marine mammals like whales produce enormous amounts of waste that can fertilize the ocean and support the growth of phytoplankton.
Understanding The Shark’S Digestive System
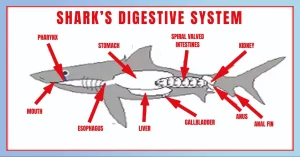
Understanding the anatomy and function of the shark’s digestive system gives us insight into how these incredible creatures process their food. From their powerful stomachs to their specialized teeth, sharks have evolved to thrive in their underwater world.
Anatomy And Function Of The Shark’S Digestive System
Sharks, one of the ocean’s most fascinating creatures, have a unique and efficient digestive system.
Sharks have a streamlined body shape with a powerful jaw and rows of sharp teeth, ideally suited for hunting and feeding. One of the key components of the shark’s digestive system is their powerful stomach. It has the ability to expand, allowing them to consume large prey. The stomach contains strong gastric acids that aid in the digestion of the shark’s food. These acids break down the prey into smaller, more manageable pieces.
After digestion, the food moves into the shark’s intestines, where nutrient absorption takes place. The intestines of a shark are relatively short compared to other animals. This allows for efficient energy extraction from their diet, which primarily consists of proteins and fats.
Waste material, also known as shark poop, is produced as the indigestible parts of the prey pass through the digestive system. Sharks eliminate waste through an opening called the cloaca, located at the base of their tail. This opening serves as an exit for both solid waste and reproductive fluids.
The Role Of The Specialized Teeth In The Digestive Process
Shark teeth are designed to grasp and tear apart prey. Different shark species have teeth specifically adapted to their unique feeding habits and diet. Some sharks have serrated teeth, which are perfect for slicing through the tough skin and flesh of their prey. Other sharks have needle-like teeth that are excellent for catching and securing slippery prey, like fish.
As sharks consume their prey, the teeth do not chew the food but rather hold it in place while the powerful jaw muscles work to tear it apart. The torn-up chunks of food then enter the shark’s stomach, where the digestive process begins. Once the prey is sufficiently broken down, the stomach acids break it down further, ensuring the efficient extraction of nutrients. The role of these specialized teeth is essential in making the digestion process more effective and efficient for sharks.
Dissecting Shark Poop: What Does It Tell Us?
Shark poop might not be your typical conversation starter, but it plays an important role in scientific research.
Studying The Composition Of Shark Poop For Scientific Research
One peculiar aspect of their biology that has piqued interest is their waste. Yes, you read that right. Sharks do poop! While it may not be the most glamorous topic, dissecting shark poop can actually provide valuable insights into their diet, ecosystem health, and even population dynamics.
Here are some key points to consider when studying the composition of shark poop for scientific research:
- Understanding the diet: By analyzing shark waste, scientists can determine what these marine predators have been eating. This information helps us gain insights into their feeding habits, preferred prey, and potential changes in their diet over time.
- Insights into the ecosystem: Shark poop can also provide clues about the overall health of the ecosystem they inhabit. It may reveal the presence of certain species or even highlight environmental changes that may impact the food chain.
- Tracking migration patterns: Since different shark species inhabit different areas of the world, studying their waste can help researchers track their movement and migration patterns. This knowledge is crucial for conservation efforts and understanding their overall behavior.
- Estimating population size: Analyzing the composition of shark waste can provide valuable data for estimating population size. By identifying and quantifying certain markers in their fecal matter, scientists can get a clearer picture of the number of sharks in a particular region.
- Assessing human impact: Shark poop analysis can also shed light on the impact of human activities on these marine creatures. For instance, detecting pollutants or microplastics in their waste can help identify areas where conservation efforts need to be focused.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Sharks Poop?
Sharks expel waste through their cloaca, an opening that serves as an exit for both waste and reproductive fluids.
Is Shark Poop Dangerous?
Shark poop is generally not dangerous to humans as it gets diluted and dispersed quickly in the vastness of the ocean.
What Does Shark Poop Look Like?
Shark poop, also known as fecal matter, can vary in appearance depending on the species. It is often large, slimy, and brownish in color.
How Often Do Sharks Poop?
The frequency of shark pooping varies among species, but it can be quite frequent, especially after a meal. Sharks are efficient eaters, so waste elimination is necessary for their well-being.
Conclusion
Sharks do indeed poop. Although their excretion process may differ from that of other animals, sharks play a crucial role in maintaining the overall health of marine ecosystems. Their waste products, released in the form of feces, contain vital nutrients that contribute to the nutrient cycle of the ocean.
The frequency and composition of shark poop vary among species, depending on their diet, size, and metabolic rate. These factors also determine the impact of their waste on the environment. As predators at the top of the food chain, sharks help regulate population sizes and maintain a balance in aquatic communities.